When completing any DIY project, choosing suitable fasteners is one of the most critical factors. Fasteners ensure that our projects are sturdy, secure, and long-lasting. From minor household repairs to large-scale constructions, using the best fasteners can make all the difference. With the wide variety of fasteners in the market today, deciding which ones are the best for our specific projects can be overwhelming. This article will discuss critical factors when choosing fasteners for your DIY projects.
Material

The first factor to consider when selecting fasteners is the material they are made of. Different materials have different properties and perform differently in various conditions. Commonly used materials for fasteners include steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, titanium, and silicon bronze. Steel fasteners are solid and affordable but can rust if not coated with anti-corrosion material. Stainless steel fasteners are highly corrosion-resistant and ideal for outdoor and marine projects. Aluminum is lightweight but not as strong as steel, while brass has excellent electrical conductivity. Titanium fasteners are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio but can be expensive. Silicon bronze screws, made of copper and zinc alloy with trace amounts of silicon, have superior corrosion resistance and are commonly used in marine and outdoor applications. Choosing the suitable material for your fasteners depends on the project requirements, environment, and budget.
Size
The size of fasteners is another crucial factor to consider when selecting the best ones for DIY projects. Fastener size is determined by its diameter, length, and thread pitch. As a general rule, the larger the diameter and length of the fastener, the higher its load-carrying capacity. Thread pitch refers to the number of threads per inch or millimeter on the screw. Fine-threaded screws have more threads per unit length than coarse-threaded ones, providing better-holding power but requiring more effort to drive in. The size of the fastener needed depends on the project’s weight-bearing requirements and the thickness of the materials being joined. It is best to consult a size chart or seek professional guidance when selecting fasteners for your DIY projects.
Head type
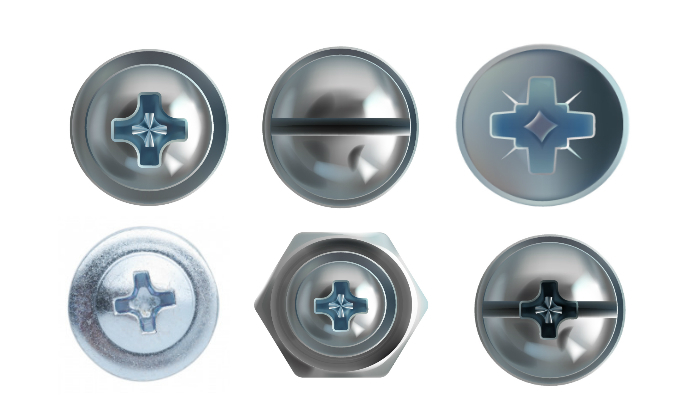

The type of head on a fastener directly affects its appearance, functionality, and ease of use. Common types include flat head, round head, pan head, truss head, hex head, and square head. Flat heads sit flush with the surface and are ideal for countersunk holes, while round and pan heads protrude slightly and have a more comprehensive bearing surface. Truss heads, commonly used in sheet metal applications, have a low profile and a wide, flat-bearing surface. Hex and square-headed fasteners require special tools such as a wrench or pliers to drive them in. When selecting a head type, consider your project’s design, aesthetic, and available tools. Matching the head type with the corresponding driver is essential for easier installation.
Drive type
The drive type refers to the shape of the recess on the fastener’s head that allows for driving it into place. Common types include slotted, Phillips, square, hex, and star drives. Slotted drives are the most traditional but require a flathead screwdriver, which can slip out easily and cause damage. Phillips drives require a specialized driver with a cross-shaped tip, providing better torque transfer and reducing slippage. Square or hex drivers provide a better grip on the fastener head but may require more effort to loosen or tighten. Star drives, or Torx, have a unique six-pointed star-shaped recess that provides excellent torque transfer and prevents slipping. When choosing the drive type, consider the ease of use, availability of drivers, and potential for slippage or damage.
Coating
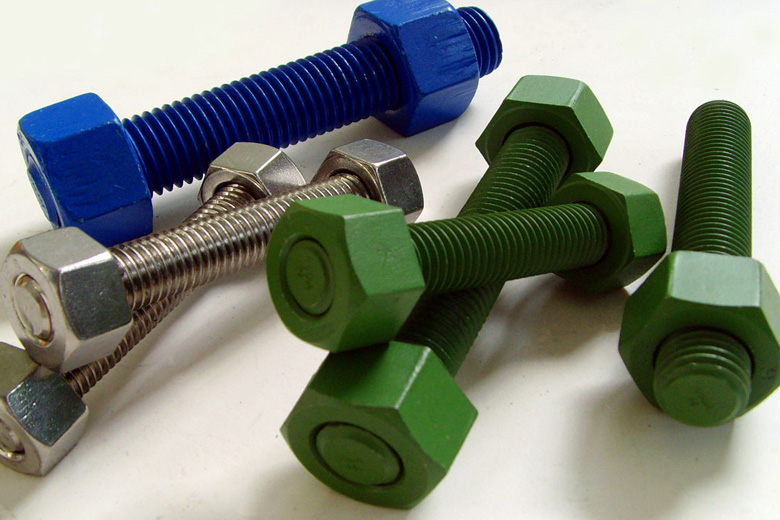
Fastener coatings are essential for protecting them from corrosion and increasing their lifespan. Standard coatings include zinc plating, galvanizing, black oxide, and powder coating. Zinc plating provides a thin layer of zinc on the fastener’s surface, protecting it from corrosion and giving it a shiny finish. Galvanizing involves dipping the fastener in molten zinc to create a thicker protective layer more resistant to harsh environments. Black oxide coating provides a black finish and enhanced corrosion resistance, ideal for indoor applications. Powder coating involves applying powdered paint to the fastener’s surface and baking it, resulting in a durable and scratch-resistant finish. Consider the project’s environment and potential exposure to elements when selecting a suitable coating. It is also essential to ensure that the coating is compatible with the material of the fastener.
Application
Another critical factor to consider when choosing fasteners for DIY projects is their intended application. Some fasteners are designed for specific purposes, such as wood screws for joining wooden materials or masonry anchors for attaching items to concrete walls. Using fasteners with high corrosion resistance for outdoor and marine projects, such as stainless steel or silicon bronze screws, is crucial. In contrast, indoor applications may require less durable fasteners like zinc-plated or black oxide-coated steel screws. For electrical projects, brass fasteners with excellent conductivity are ideal. Consider the project’s weight-bearing requirements and environmental factors when selecting the most suitable fastener for your DIY project. It is also essential to ensure that the fastener’s material, size, and coating are suitable for the intended application.

